Section 2.4 Continuity
Learning Objectives.
Explain the three conditions for continuity at a point.
Describe three kinds of discontinuities.
Define continuity on an interval.
Provide an example of the intermediate value theorem.
Many functions have the property that their graphs can be traced with a pencil without lifting the pencil from the page. Such functions are called continuous. Other functions have points at which a break in the graph occurs, but satisfy this property over intervals contained in their domains. They are continuous on these intervals and are said to have a discontinuity at a point where a break occurs.
We begin our investigation of continuity by exploring what it means for a function to have continuity at a point. Intuitively, a function is continuous at a particular point if there is no break in its graph at that point.
Subsection 2.4.1 Continuity at a Point
Before we look at a formal definition of what it means for a function to be continuous at a point, let’s consider various functions that fail to meet our intuitive notion of what it means to be continuous at a point. We then create a list of conditions that prevent such failures.
Our first function of interest is shown in Figure 2.88. We see that the graph of \(f(x)\) has a hole at \(a\text{.}\) In fact, \(f(a)\) is undefined. At the very least, for \(f(x)\) to be continuous at \(a\text{,}\) we need the following condition:
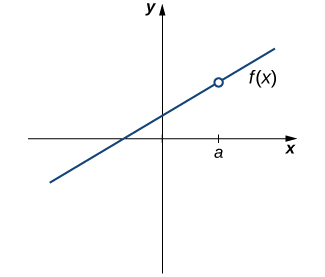
However, as we see in Figure 2.89, this condition alone is insufficient to guarantee continuity at the point \(a\text{.}\) Although \(f(a)\) is defined, the function has a gap at \(a\text{.}\) In this example, the gap exists because \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)}\) does not exist. We must add another condition for continuity at \(a\)—namely,
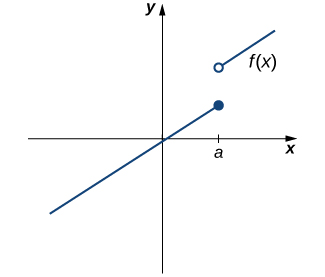
However, as we see in Figure 2.90, these two conditions by themselves do not guarantee continuity at a point. The function in this figure satisfies both of our first two conditions, but is still not continuous at \(a\text{.}\) We must add a third condition to our list:
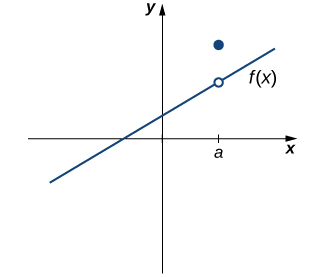
Now we put our list of conditions together and form a definition of continuity at a point.
Definition 2.91.
A function \(f(x)\) is continuous at a point \(a\) if and only if the following three conditions are satisfied:
\(f(a)\) is defined
\(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)}\) exists
\(\displaystyle \lim_{x\to a}f(x)=f(a)\)
A function is discontinuous at a point \(a\) if it fails to be continuous at \(a\text{.}\)
The following procedure can be used to analyze the continuity of a function at a point using this definition.
Note 2.92. Problem-Solving Strategy: Determining Continuity at a Point.
Check to see if \(f(a)\) is defined. If \(f(a)\) is undefined, we need go no further. The function is not continuous at \(a\text{.}\) If \(f(a)\) is defined, continue to step 2.
Compute \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x).}\) In some cases, we may need to do this by first computing \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x).}\) If \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)}\) does not exist (that is, it is not a real number), then the function is not continuous at \(a\) and the problem is solved. If \(\lim_{x\to a}f(x)\) exists, then continue to step 3.
Compare \(f(a)\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x).}\) If \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)\neq f(a),}\) then the function is not continuous at \(a\text{.}\) If \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)=f(a),}\) then the function is continuous at \(a\text{.}\)
The next three examples demonstrate how to apply this definition to determine whether a function is continuous at a given point. These examples illustrate situations in which each of the conditions for continuity in the definition succeed or fail.
Example 2.93. Determining Continuity at a Point, Condition 1.
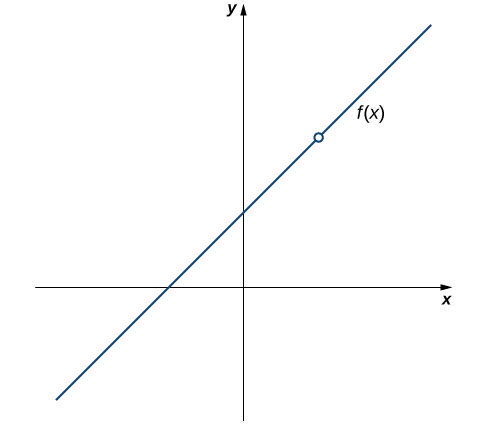
Using the definition, determine whether the function \(f(x)=(x^2-4)/(x-2)\) is continuous at \(x=2.\) Justify the conclusion.
Let’s begin by trying to calculate \(f(2).\) We can see that \(f(2)=0/0,\) which is undefined. Therefore, \(f(x)=\frac{x^2-4}{x-2}\) is discontinuous at 2 because \(f(2)\) is undefined. The graph of \(f(x)\) is shown in Figure 2.94.
Example 2.95. Determining Continuity at a Point, Condition 2.
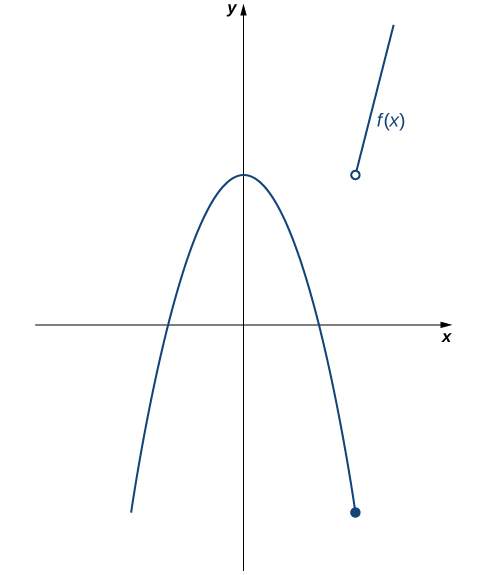
Using the definition, determine whether the function \(f(x)=\begin{cases}-x^2+4\amp\text{ if } x\leq 3\\4x-8\amp\text{ if } x\gt 3 \end{cases}\) is continuous at \(x=3.\) Justify the conclusion.
Let’s begin by trying to calculate \(f(3).\)
Thus, \(f(3)\) is defined. Next, we calculate \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3}f(x).}\) To do this, we must compute \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3^-}f(x)}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3^+}f(x)}\text{ : }\)
and
Therefore, \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3}f(x)}\) does not exist. Thus, \(f(x)\) is not continuous at 3. The graph of \(f(x)\) is shown in Figure 2.96.
Example 2.97. Determining Continuity at a Point, Condition 3.
Using the definition, determine whether the function \(f(x)=\begin{cases} \frac{x^2-4x+3}{x-1}\amp\text{ if } x\neq 1 \\ -2\amp\text{ if } x=1 \end{cases}\) is continuous at \(x=1.\)
First, observe that
Next,
Last, compare \(f(1)\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 1}f(x).}\) We see that
Since all three of the conditions in the definition of continuity are satisfied, \(f(x)\) is continuous at \(x=1.\)
Checkpoint 2.98.
Using the definition, determine whether the function \(f(x)=\begin{cases}2x+1\amp\text{ if } x\lt 1\\2\amp\text{ if } x=1\\-x+4\amp\text{ if } x\gt 1 \end{cases}\) is continuous at \(x=1.\) If the function is not continuous at 1, indicate the condition for continuity at a point that fails to hold.
By applying the definition of continuity and previously established theorems concerning the evaluation of limits, we can state the following theorem.
Theorem 2.99. Continuity of Polynomials and Rational Functions.
Polynomials and rational functions are continuous at every point in their domains.
Proof.
Previously, we showed that if \(p(x)\) and \(q(x)\) are polynomials, \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}p(x)=p(a)}\) for every polynomial \(p(x)\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}\frac{p(x)}{q(x)}=\frac{p(a)}{q(a)}}\) as long as \(q(a)\neq 0.\) Therefore, polynomials and rational functions are continuous on their domains.
We now apply Theorem 2.99 to determine the points at which a given rational function is continuous.
Example 2.100. Continuity of a Rational Function.
For what values of \(x\) is \(f(x)=\frac{x+1}{x-5}\) continuous?
The rational function \(f(x)=\frac{x+1}{x-5}\) is continuous for every value of \(x\) except \(x=5.\)
Checkpoint 2.101.
For what values of \(x\) is \(f(x)=3x^4-4x^2\) continuous?
Subsection 2.4.2 Types of Discontinuities
As we have seen in Example 2.93 and Example 2.95, discontinuities take on several different appearances. We classify the types of discontinuities we have seen thus far as removable discontinuities, infinite discontinuities, or jump discontinuities. Intuitively, a removable discontinuity is a discontinuity for which there is a hole in the graph, a jump discontinuity is a noninfinite discontinuity for which the sections of the function do not meet up, and an infinite discontinuity is a discontinuity located at a vertical asymptote. Figure 2.102 illustrates the differences in these types of discontinuities. Although these terms provide a handy way of describing three common types of discontinuities, keep in mind that not all discontinuities fit neatly into these categories.
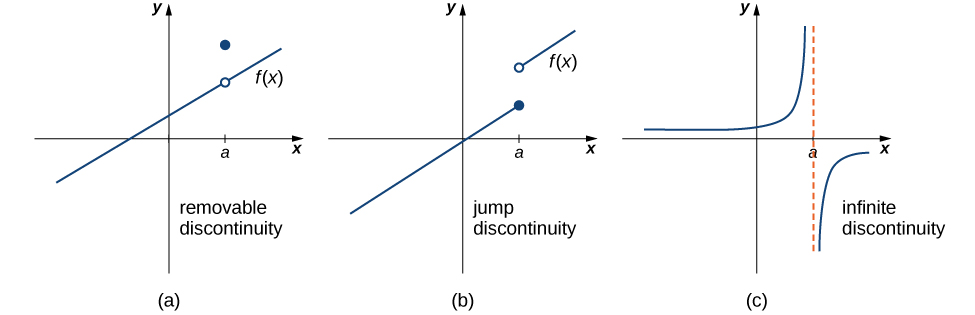
These three discontinuities are formally defined as follows:
Definition 2.103.
If \(f(x)\) is discontinuous at \(a\text{,}\) then
\(f\) has a removable discontinuity at \(a\) if \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)}\) exists. (Note: When we state that \(\displaystyle{\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)}}\) exists, we mean that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}f(x)=L,}\) where \(L\) is a real number.)
\(f\) has a jump discontinuity at \(a\) if \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)}\) both exist, but \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)\neq \lim_{x\to a^+}f(x).}\) (Note: When we state that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)}\) both exist, we mean that both are real-valued and that neither take on the values \(\pm\infty\) .)
\(f\) has an infinite discontinuity at \(a\) if \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)=\pm \infty }\) or \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)=\pm \infty .}\)
Example 2.104. Classifying a Discontinuity.
In Example 2.93, we showed that \(f(x)=\frac{x^2-4}{x-2}\) is discontinuous at \(x=2.\) Classify this discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
To classify the discontinuity at 2 we must evaluate \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 2}f(x)}\text{ : }\)
Since \(f\) is discontinuous at 2 and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 2}f(x)}\) exists, \(f\) has a removable discontinuity at \(x=2.\)
Example 2.105. Classifying a Discontinuity.
In Example 2.95, we showed that \(f(x)=\begin{cases}-x^2+4\amp\text{ if } x\leq 3\\4x-8\amp\text{ if } x\gt 3\end{cases}\) is discontinuous at \(x=3.\) Classify this discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
Earlier, we showed that \(f\) is discontinuous at 3 because \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3}f(x)}\) does not exist. However, since \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3^-}f(x)=-5}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 3^+}f(x)=4}\) both exist, we conclude that the function has a jump discontinuity at 3.
Example 2.106. Classifying a Discontinuity.
Determine whether \(f(x)=\frac{x+2}{x+1}\) is continuous at -1. If the function is discontinuous at -1, classify the discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
The function value \(f(-1)\) is undefined. Therefore, the function is not continuous at -1. To determine the type of discontinuity, we must determine the limit at -1. We see that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to -1^-}\frac{x+2}{x+1}=-\infty }\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to -1^+}\frac{x+2}{x+1}=+\infty .}\) Therefore, the function has an infinite discontinuity at -1.
Checkpoint 2.107.
For \(f(x)=\begin{cases}x^2\amp\text{ if } x\neq 1\\3\amp\text{ if } x=1 \end{cases},\) decide whether \(f\) is continuous at 1. If \(f\) is not continuous at 1, classify the discontinuity as removable, jump, or infinite.
Subsection 2.4.3 Continuity over an Interval
Now that we have explored the concept of continuity at a point, we extend that idea to continuity over an interval. As we develop this idea for different types of intervals, it may be useful to keep in mind the intuitive idea that a function is continuous over an interval if we can use a pencil to trace the function between any two points in the interval without lifting the pencil from the paper. In preparation for defining continuity on an interval, we begin by looking at the definition of what it means for a function to be continuous from the right at a point and continuous from the left at a point.
Note 2.108. Continuity from the Right and from the Left.
A function \(f(x)\) is said to be continuous from the right at \(a\) if \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)=f(a).}\)
A function \(f(x)\) is said to be continuous from the left at \(a\) if \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^-}f(x)=f(a).}\)
A function is continuous over an open interval if it is continuous at every point in the interval. A function \(f(x)\) is continuous over a closed interval of the form \([a,b]\) if it is continuous at every point in \((a,b)\) and is continuous from the right at \(a\) and is continuous from the left at \(b\text{.}\) Analogously, a function \(f(x)\) is continuous over an interval of the form \((a,b]\) if it is continuous over \((a,b)\) and is continuous from the left at \(b\text{.}\) Continuity over other types of intervals are defined in a similar fashion.
Requiring that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)=f(a)}\) and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to b^-}f(x)=f(b)}\) ensures that we can trace the graph of the function from the point \((a,f(a))\) to the point \((b,f(b))\) without lifting the pencil. If, for example, \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)\neq f(a),}\) we would need to lift our pencil to jump from \(f(a)\) to the graph of the rest of the function over \((a,b].\)
Example 2.109. Continuity on an Interval.
State the interval(s) over which the function \(f(x)=\frac{x-1}{x^2+2x}\) is continuous.
Since \(f(x)=\frac{x-1}{x^2+2x}\) is a rational function, it is continuous at every point in its domain. The domain of \(f(x)\) is the set \((-\infty ,-2)\cup (-2,0)\cup (0,+\infty ).\) Thus, \(f(x)\) is continuous over each of the intervals \((-\infty ,-2),(-2,0),\) and \((0,+\infty ).\)
Example 2.110. Continuity over an Interval.
State the interval(s) over which the function \(f(x)=\sqrt{4-x^2}\) is continuous.
From the limit laws, we know that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to a}\sqrt{4-x^2}=\sqrt{4-a^2}}\) for all values of \(a\) in \((-2,2).\) We also know that \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to -2^+}\sqrt{4-x^2}=0}\) exists and \(\displaystyle{\lim_{x\to 2^-}\sqrt{4-x^2}=0}\) exists. Therefore, \(f(x)\) is continuous over the interval \([-2,2].\)
Checkpoint 2.111.
State the interval(s) over which the function \(f(x)=\sqrt{x+3}\) is continuous.
Subsection 2.4.4 The Intermediate Value Theorem
Functions that are continuous over intervals of the form \([a,b],\) where \(a\) and \(b\) are real numbers, exhibit many useful properties. Throughout our study of calculus, we will encounter many powerful theorems concerning such functions. The first of these theorems is the Intermediate Value Theorem.
Theorem 2.112. The Intermediate Value Theorem.
Let \(f\) be continuous over a closed, bounded interval \([a,b].\) If \(z\) is any real number between \(f(a)\) and \(f(b),\) then there is a number \(c\) in \([a,b]\) satisfying \(f(c)=z\) in Figure 2.113.
!["A diagram illustrating the intermediate value theorem. There is a generic continuous curved function shown over the interval [a,b]. The points fa. and fb. are marked, and dotted lines are drawn from a, b, fa., and fb. to the points (a, fa.) and (b, fb.). A third point, c, is plotted between a and b. Since the function is continuous, there is a value for fc. along the curve, and a line is drawn from c to (c, fc.) and from (c, fc.) to fc., which is labeled as z on the y axis."](external/CNX_Calc_Figure_02_04_007.jpg)
Example 2.114. Application of the Intermediate Value Theorem.
Show that \(f(x)=x^2-11x+10\) has at least one zero.
Since \(f(x)=x^2-11x+10\) is continuous over \((-\infty ,+\infty ),\) it is continuous over any closed interval of the form \([a,b].\) If you can find an interval \([a,b]\) such that \(f(a)\) and \(f(b)\) have opposite signs, you can use the Intermediate Value Theorem to conclude there must be a real number \(c\) in \((a,b)\) that satisfies \(f(c)=0.\) Note that
and
Using the Intermediate Value Theorem, we can see that there must be a real number \(c\) in \([0,2]\) that satisfies \(f(c)=0.\) Therefore, \(f(x)=x^2-11x+10\) has at least one zero.
Example 2.115. When Can You Apply the Intermediate Value Theorem?
If \(f(x)\) is continuous over \([0,2],f(0)\gt 0\) and \(f(2)\gt 0,\) can we use the Intermediate Value Theorem to conclude that \(f(x)\) has no zeros in the interval \([0,2\text{ ]? }\) Explain.
No. The Intermediate Value Theorem only allows us to conclude that we can find a value between \(f(0)\) and \(f(2);\) it doesn’t allow us to conclude that we can’t find other values. To see this more clearly, consider the function \(f(x)=(x-1)^2.\) It satisfies \(f(0)=1\gt 0,f(2)=1\gt 0,\) and \(f(1)=0.\)
Example 2.116. When Can You Apply the Intermediate Value Theorem?
For \(f(x)=1/x,f(-1)=-1\lt 0\) and \(f(1)=1\gt 0.\) Can we conclude that \(f(x)\) has a zero in the interval \([-1,1]?\)
No. The function is not continuous over \([-1,1].\) The Intermediate Value Theorem does not apply here.
Checkpoint 2.117.
Show that \(f(x)=x^3-x^2-3x+1\) has a zero over the interval \([0,1].\)
Subsection 2.4.5 Key Concepts
For a function to be continuous at a point, it must be defined at that point, its limit must exist at the point, and the value of the function at that point must equal the value of the limit at that point.
Discontinuities may be classified as removable, jump, or infinite.
A function is continuous over an open interval if it is continuous at every point in the interval. It is continuous over a closed interval if it is continuous at every point in its interior and is continuous at its endpoints.
The Intermediate Value Theorem guarantees that if a function is continuous over a closed interval, then the function takes on every value between the values at its endpoints.
This book is a custom edition based on OpenStax Calculus Volume 1. You can download the original for free at https://openstax.org/details/books/calculus-volume-1.